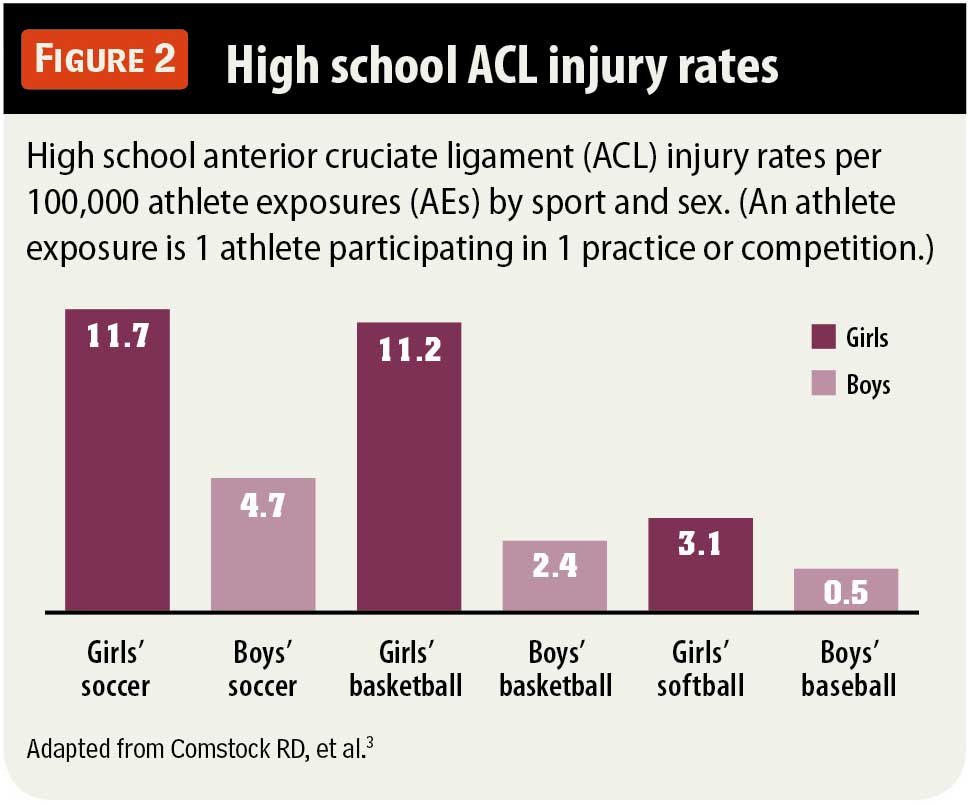
ACL Injury Rates in Women Athletes: Exploring Key Factors
ACL injury rates in women athletes have emerged as a critical topic in sports science, highlighting the stark gender differences in sports injuries. Recent studies indicate that female athletes suffer from ACL tears at a rate 1.7 times higher than their male counterparts, prompting discussions about the underlying factors contributing to these disparities. While it’s commonly assumed that biological differences, such as hormonal fluctuations and anatomical variations, play a significant role, new research suggests that social factors may be equally, if not more, influential. Understanding ACL injury prevention is essential, as the current metrics used to gauge athlete exposure often reflect systemic inequities in sports, making women’s injury risks appear even higher. By exploring these dimensions, we can better strategize around injury management and create safer environments for women in sports.
The prevalence of anterior cruciate ligament injuries among female athletes has raised alarm bells in recent years, warranting an in-depth examination of injury patterns and contributing factors. Higher rates of knee injuries in women, often attributed to physiological and anatomical traits, require a critical reassessment of traditional perspectives that overlook significant social contexts. With rising concerns surrounding sports injuries in women’s leagues, athletes and coaches are increasingly seeking effective ACL injury prevention strategies tailored to female players’ unique circumstances. A refined understanding of athlete exposure metrics could unveil crucial insights into how resource disparities in training and competition impact injury rates. By addressing the broader social dynamics at play, we pave the way for transformative changes in how women’s sports injuries are analyzed and mitigated.
Understanding ACL Injury Rates in Women Athletes
ACL injury rates have been a pressing issue in women’s sports, with recent studies indicating that women athletes suffer from ACL injuries at a rate approximately 1.7 times higher than their male counterparts. This discrepancy is often attributed to biological factors, such as hormonal differences and anatomical structures, but emerging research highlights critical social factors that may contribute significantly to this issue. For instance, women commonly play in smaller teams and experience higher involvement in active competition, factors that can lead to increased strain on their bodies and, subsequently, higher injury risks.
Moreover, the way injury data has traditionally been measured may obscure these disparities further. The terms ‘athlete exposures’ often fail to consider the unique conditions under which female athletes train and compete. By merely calculating exposures based on the number of athletes and game metrics, crucial variables such as practice time versus game time and individual athlete conditioning are overlooked, making it difficult to develop effective ACL injury prevention strategies tailored for women’s sports.
Social Factors Influencing Women’s Sports Injuries
Social factors play a crucial role in the rate of injuries among women athletes, particularly regarding access to training and resources. Underfunding of women’s sports leads to fewer training hours, less exposure to coaching, and inadequate injury prevention programs. This inequity means that even if women train similarly to men in high-pressure settings, their overall preparation may be lacking due to fewer resources, increasing their likelihood of sustaining injuries, including ACL tears.
Additionally, the distribution of participation in women’s sports is often skewed, leading to smaller team sizes. This can create a false perception of injury risk when comparing male and female athletes. For example, fewer participants on women’s teams may lead to individual athletes receiving less variability in practice activities, potentially jeopardizing their physical conditioning and increasing injury rates. Understanding these social dynamics is essential for developing a comprehensive approach to injury prevention in women’s sports.
The Impact of Team Size on ACL Injury Risk
Team size significantly affects the dynamics of sports and the corresponding injury rates, particularly for ACL injuries among women athletes. Research has shown that smaller teams lead to increased playtime for individual athletes, resulting in higher exposure to injury-causing situations. Unlike their male counterparts, who often benefit from larger rosters and, as a result, more balanced playtime distribution, female athletes frequently bear a heavier burden during competition, raising their likelihood of sustaining serious injuries such as ACL tears.
The metrics used to calculate injury rates must consider these differences in team composition. For instance, if a smaller women’s team trains less frequently due to fewer roster players, the risk per participant during games can skyrocket. This highlights the necessity for tailored exposure metrics that account for team size and the specific context in which women athletes compete, offering a more accurate picture of ACL injury risk and prevention strategies.
Revising Athlete Exposure Metrics for Injury Prevention
Revising athlete exposure metrics is crucial for accurately reflecting injury risks and preventing ACL injuries in women’s sports. Traditional metrics often rely on simple calculations that aggregate player numbers with total games played. However, these do not account for individual participation levels or the crucial distinction between time spent in practice versus competition, where the risk of injury is significantly heightened. Adjusting these metrics to reflect individual exposure will provide a clearer insight into each athlete’s risk profile.
Furthermore, incorporating factors such as access to quality facilities, coaching support, and therapeutic resources into athlete exposure calculations will enhance our understanding of ACL injury dynamics in women’s sports. By acknowledging and addressing the role of these structural factors, sports science can aim to create equitable and effective methods for injury prevention tailored to the unique experiences of female athletes, helping to reduce the ACL injury rates that currently burden them.
The Role of Proper Conditioning in Preventing ACL Injuries
Proper conditioning is one of the key factors in preventing ACL injuries among athletes, especially women who are often disadvantaged by limited training opportunities. Research indicates that injuries are far more likely to occur during games as opposed to practice sessions, underscoring the importance of conditioning that closely resembles game situations. Female athletes typically spend less time in competitive environments compared to their male counterparts, leading to potential inadequacies in their preparedness for high-stress situations that could lead to injuries.
Enhancing training regimes to focus on strength, agility, and conditioning can significantly reduce injury risks. Implementing comprehensive training programs that are gender-specific, addressing the needs of female athletes in their unique competition contexts, will help bridge the gap in injury rates. By emphasizing the importance of proper conditioning alongside biomechanical considerations, sports scientists and coaches can take proactive measures to safeguard women’s health in sports and reduce ACL injury occurrences.
Advancing Research into Gendered Sports Injury Dynamics
Advancing research into the gendered dynamics of sports injuries is vital for developing effective injury prevention strategies. Current literature suggests that ACL injuries are not merely a consequence of biological differences between genders but are significantly influenced by social and structural inequities in sports. By encouraging more in-depth investigations into how these factors align with injury rates, particularly for women athletes, the sports community can begin to address the root causes of higher injury prevalence.
The integration of quantitative and qualitative research methodologies can enrich our understanding of ACL injuries in women. These studies ought to include diverse variables such as athlete exposure levels, training environments, and social factors affecting participation in sports. By painting a comprehensive picture of the unique challenges that women face, we can inform better policies and practices that not only seek to mitigate injury risks but also promote equity in participation and training methods across genders.
Innovations in ACL Injury Prevention Techniques
Emerging innovations in ACL injury prevention techniques offer hope for reducing the rates of injury among female athletes. Research directed towards developing tailored training programs has become increasingly critical, as it allows for the design of workouts that specifically target the strengths and weaknesses inherent in female physiology. Techniques such as neuromuscular training and plyometric exercises focus on enhancing stability and strength around the knee joint, which is crucial for preventing injuries.
Additionally, advancements in technology, such as wearable devices, can track athlete movements and predict injury risks in real-time. These tools can provide insight into an athlete’s performance metrics, helping trainers to pinpoint areas needing improvement. By implementing proactive injury prevention techniques grounded in the latest sports science, we can significantly decrease the incidents of ACL injuries among women athletes, extending their careers and enhancing their overall performance.
The Importance of Education and Awareness in Women’s Sports
Education and awareness are critical components in addressing the high rates of ACL injuries in women athletes. Coaches, medical staff, and athletes themselves must be aware of the specific risks associated with women’s sports and the multifaceted factors contributing to these injuries. By fostering an informed sports culture that prioritizes injury prevention, teams can help create safer athletics environments for female athletes.
Programs aimed at educating athletes on how to warm up properly, strengthen key muscle groups, and recognize early signs of injuries can empower women in sports. This proactive approach not only raises awareness but fosters a culture of prevention, where female athletes are equipped with the knowledge and skills necessary to protect themselves from potential injuries such as ACL tears.
Policy Changes Needed to Support Women’s Sports
Policy changes are necessary to support the health and safety of women athletes, particularly concerning injuries like ACL tears. Institutions and organizations should advocate for increased funding and resources directed at women’s sports. Enhanced investment can lead to better facilities, improved training programs, and greater access to medical support, which can all contribute to lowering injury rates.
Moreover, establishing more equitable standards for women’s sports, such as ensuring similar training facilities and medical provisions as their male counterparts, can be a game changer. These policy reforms not only enhance the competitive landscape for female athletes but also promote an environment in which injuries can be systematically reduced, thereby addressing the disparities currently seen in ACL injury rates between genders.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the ACL injury rates in women athletes compared to men?
Studies show that ACL injury rates in women athletes are approximately 1.7 times higher than those in men. This discrepancy is attributed to both biological and sociocultural factors, including differences in team sizes and athlete exposure metrics.
How do athlete exposure metrics affect ACL injury rates in women’s sports?
Athlete exposure metrics, which calculate the likelihood of injuries based on the number of athletes and practice/game time, often underestimate women’s injury risks. Due to smaller rosters and fewer training sessions, women tend to have higher injury rates during matches.
What are some ACL injury prevention strategies for female athletes?
ACL injury prevention strategies for female athletes include improving conditioning, focusing on strength training, and increasing awareness of their unique injury risks. Enhanced resources, such as access to trainers and better facilities, also play a critical role.
What role do gender differences in sports injuries play in ACL rates?
Gender differences in sports injuries significantly impact ACL rates, as women’s bodies are generally more susceptible to certain types of injuries. However, recent research emphasizes that social factors, such as training resources and support systems, also contribute to these disparities.
How can sports science improve understanding of ACL injury rates in women athletes?
Sports science can improve understanding of ACL injury rates by utilizing more accurate athlete exposure metrics that account for individual training and competition times, and by emphasizing the need for research on social inequities affecting women’s sports.
Why are ACL injury rates potentially higher in women’s ice hockey?
ACL injury rates may be higher in women’s ice hockey due to smaller rosters that result in increased playing time per athlete, as well as lesser training opportunities compared to men’s teams, leading to higher injury risks during matches.
What is the significance of hormonal cycles in relation to ACL injury rates in female athletes?
Hormonal cycles have been traditionally thought to contribute to higher ACL injury rates in female athletes, but recent research suggests that social factors and athlete exposure metrics play a more significant role in their increased risk.
How does team size influence ACL injury risks in women athletes?
Team size impacts ACL injury risks as smaller teams lead to fewer players sharing playing time, increasing individual exposure during matches and training—resulting in higher injury likelihood, despite similar per-game injury rates when compared to men.
What is the importance of access to resources for reducing ACL injury rates in women athletes?
Access to quality resources such as physical therapy, better training facilities, and effective coaching is crucial in reducing ACL injury rates in women athletes. Such resources can enhance injury prevention and improve overall athletic performance.
What recommendations are made for studying ACL injuries in female athletes?
Recommendations for studying ACL injuries in female athletes include disaggregating practice from game time in data reports, controlling for team sizes, and evaluating individual athlete exposure metrics to better understand their injury risks.
| Key Metric | Men’s Rates | Women’s Rates |
|---|---|---|
| Roster Size-based AEs | 28 | 25 |
| Participant-based AEs | 19 | 17 |
| Injury Rate per 100 Roster-based AEs | 3.6 | 4.0 |
| Injury Rate per 100 Participant-based AEs | 5.3 | 5.9 |
| Injury Risk per Team Member | 0.036 | 0.040 |
Summary
ACL injury rates in women athletes are a significant concern highlighted by recent research from Harvard’s GenderSci Lab, which challenges traditional beliefs attributing these injuries solely to biological differences. The study emphasizes that social factors, such as resource allocation and team dynamics, contribute critically to the disparity in ACL injuries. By refining the metrics used to evaluate injury risk and advocating for equitable investment in women’s sports, a clearer understanding of these high injury rates can be achieved, ultimately leading to better prevention strategies.